- info@simultura.com
- +90 312 395 25 24
- info@simultura.com
- +90 312 395 25 24
Thermomechanical characterization is a process used to study the mechanical and thermal properties of materials simultaneously. This involves analyzing how a material responds to changes in temperature while undergoing mechanical deformation or stress. The goal is to understand how temperature affects the mechanical behavior of a material and vice versa.
Key aspects of thermomechanical characterization include:
1.Mechanical Properties: This involves studying the response of a material to mechanical forces such as tension, compression, or shear. Common mechanical properties include tensile strength, yield strength, modulus of elasticity, and toughness.
2.Thermal Properties: This involves studying how a material responds to changes in temperature. Key thermal properties include coefficient of thermal expansion, thermal conductivity, specific heat capacity, and thermal diffusivity.
3.Creep and Stress Relaxation Testing: These tests involve applying a constant stress or strain to a material at an elevated temperature to study its long-term deformation behavior.
Thermomechanical characterization helps in designing materials with specific properties for different applications and understanding the behavior of materials under different environmental conditions.
Physical simulation is the exact reproduction of the thermal and mechanical processes in the laboratory that a material is subjected to during the manufacturing process or end use. Physical simulation is a valuable tool used to study metallurgical processes, develop new materials and replicate real world conditions in the laboratory.
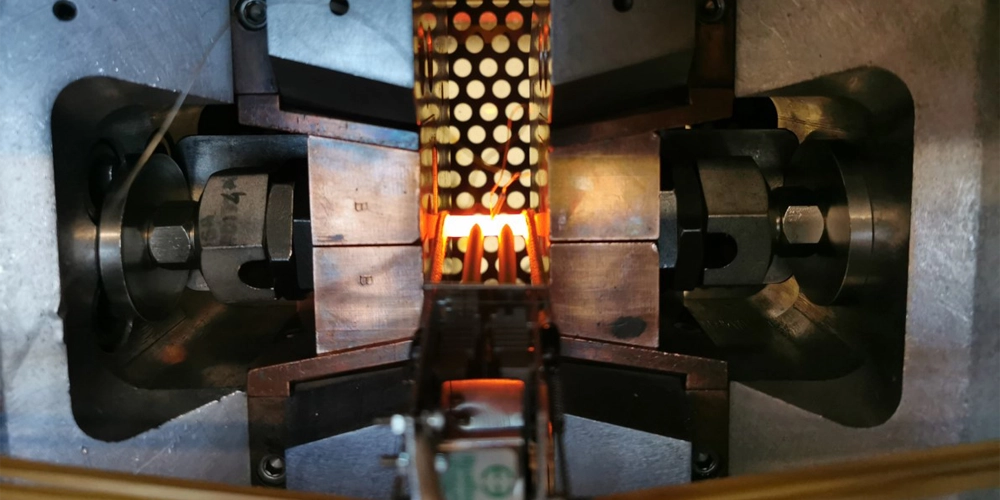
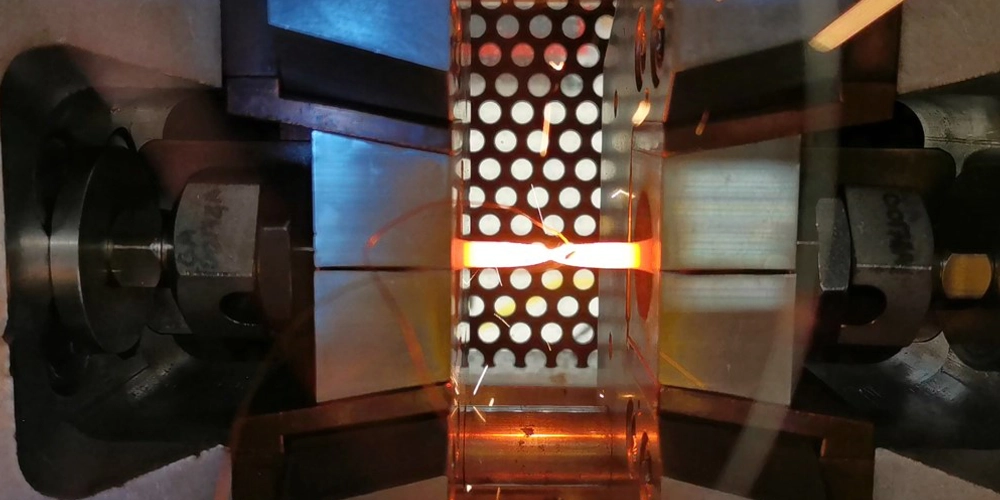

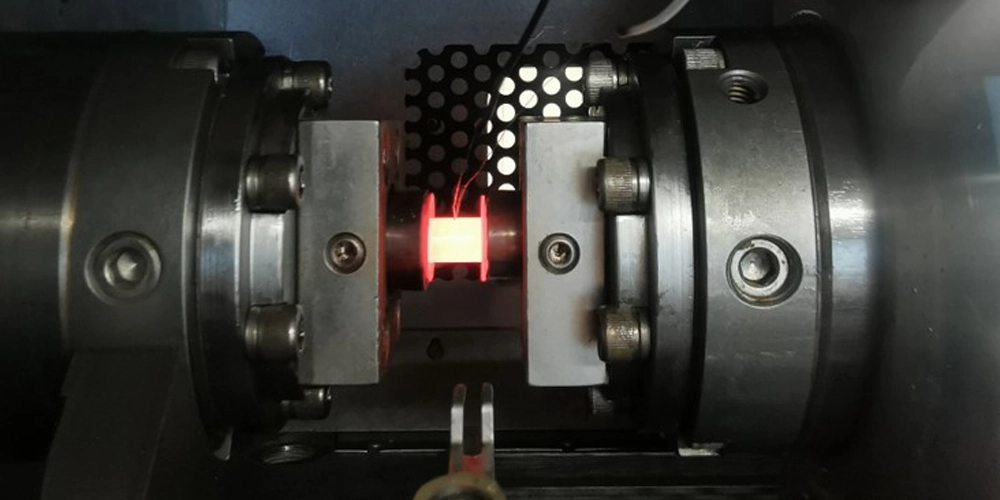

Simultura Material Technologies was established in 2019 to provide consultancy and engineering services.